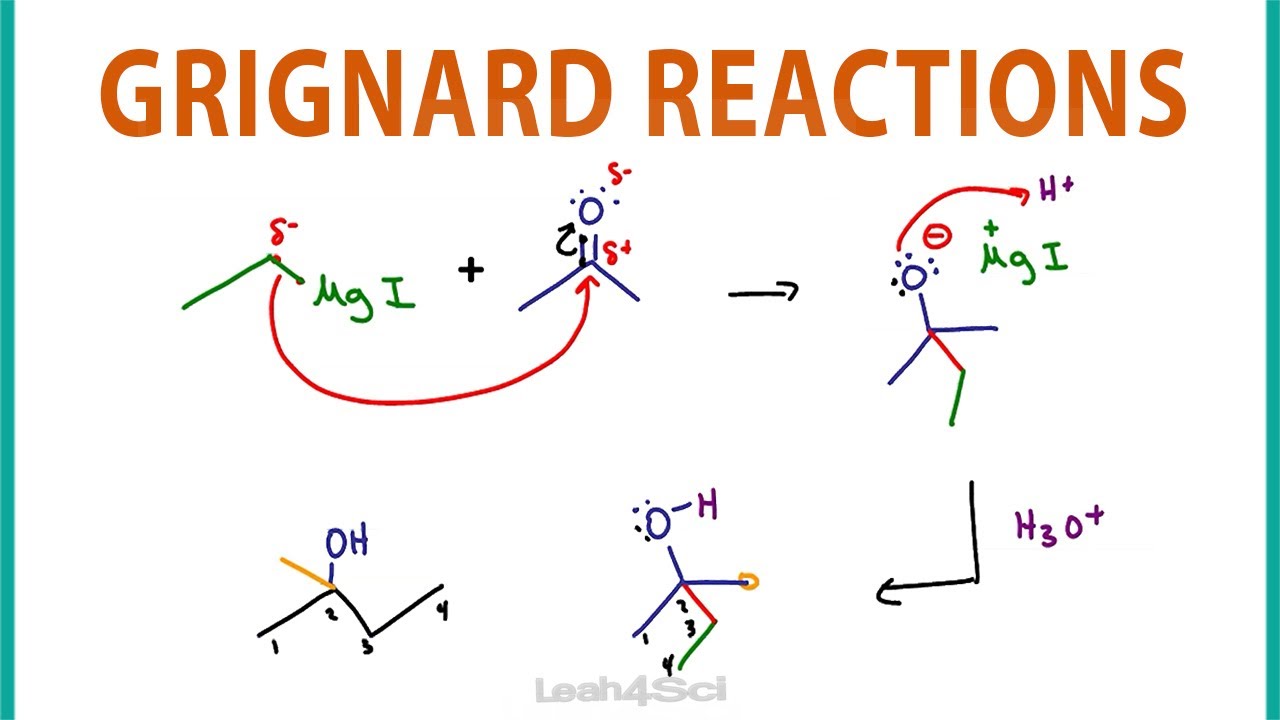
Grignard Reagent is an important class of organometallic compounds with the general formula R-Mg-X (R is alkyl or aryl and X is halogen). Due to their high reactivity, Grignard reagents have a wide range of applications in organic synthesis. The following are its main uses:
1. Carbon-carbon bond formation
Reaction with carbonyl compounds:
The reaction of Grignard reagents with aldehydes and ketones to form alcohols is an important method for the synthesis of complex organic molecules.
Example:
Formaldehyde → primary alcohol
other aldehydes → secondary alcohols
ketones → tertiary alcohols
Reaction with carbon dioxide:
Carboxylic acids are formed and used in the synthesis of organic acids and their derivatives.
2. Carbon-heteroatom bond formation
Reaction with epoxide:
Produces an alcohol, which is used in the synthesis of polyfunctional compounds.
Reaction with nitriles:
To form ketone, used for the synthesis of complex ketone compounds.
3. Synthesis of complex molecules
Synthesis of natural products:
Used to synthesize complex natural products such as vitamin A, steroids, etc.
Drug Synthesis:
Used to synthesize a variety of drug intermediates, such as antidepressants, antibiotics, etc.
4. Functionalization reaction
Reaction with halogenated hydrocarbons:
Generate new carbon-carbon bonds, used in the synthesis of complex hydrocarbon compounds.
Reaction with unsaturated bonds:
Reaction with alkenes and alkynes to generate new organic compounds.
5. Other applications
Polymer Chemistry:
Used to synthesize polymeric materials with specific structures.
Organometallic chemistry:
Participate in a variety of organometallic reactions as intermediates.
Summary
Due to their high reactivity and versatility, Grignard reagents play an important role in organic synthesis and are widely used in carbon-carbon bond formation, complex molecular synthesis and functionalization reactions.
How to make a Grignard reagent from magnesium turnings/chips?
